Click to read the article in Turkish
The Turkish Statistical Institute (TurkStat) has announced the findings of the Income and Living Conditions Survey for 2018.
In the calculation of income, the households income is converted into the equivalent household disposable income by taking into account the size and composition of the household.
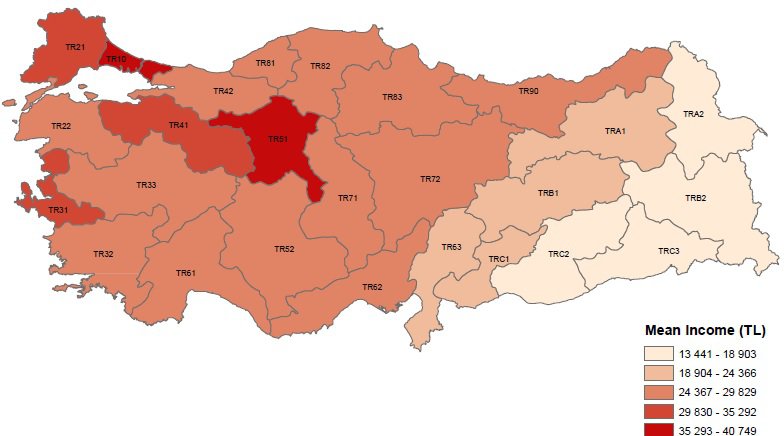
According to survey results, the share of the top quintile by the equivalised household disposable income was 46.3 percent recording a decrease of 1.3 points whilst the share of the bottom quintile was 6.2 percent with an increase of 0.1 points in comparison with the previous year.
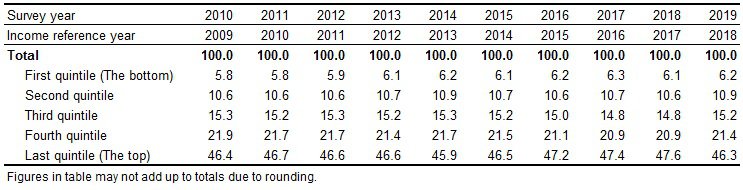
İstanbul, the largest city of the country with a population of 15.5 million, was the region having the highest mean annual equivalised household disposable income with 40 thousand 749 lira (1 US dollar = 7.47 Turkish lira), according to the survey's regional results.
It was followed by West Anatolia and Aegean regions with mean annual equivalised household disposable income 32 thousand 384 lira and 30 thousand 337 lira respectively.
Gini coefficient was 0.395
Gini coefficient, one of the measures of income inequality, varies between 0, which reflects complete equality and 1, which indicates complete inequality. According to 2019 results, Gini coefficient was estimated at 0.395 with a decrease of 0.013 points compared with the previous year.
S80/S20 ratio calculated as the ratio of total income received by the richest 20 percent of the population to that received by the poorest 20 percent of the population decreased from 7.8 to 7.4, while the S90/S10 ratio, which is calculated as the ratio of total income received by the richest 10 percent of the population to that received by the poorest 10 percent of the population decreased from 13.7 to 13.0.
Mean annual household disposable income was 59 thousand 873 lira
The mean annual household disposable income was 59 thousand 873 lira in 2019 with an increase of 16.5 percent compared to last year in Turkey.
The mean annual equivalised household disposable income increased by 17.9 percent compared to the previous year from 24 thousand 199 lira to 28 thousand 522 lira.
One person households had the highest mean annual equivalised household disposable income
According to the household type, the highest mean annual equivalised household disposable income observed among the one person households with 37 thousand 262 lira with an increase of 4 thousand 616 lira compared to last year. The mean annual equivalised household disposable income of the multi-person no-family households 32 thousand 941 lira while this income of the one-family households was 29 thousand 449 lira. The household type with the lowest mean annual equivalised disposable income was extended-family households with 22 thousand 794 lira.
Wages and salaries held the highest proportion of total income with 46.7 percent
The ratio of wage and salaries got the highest rate with 46.7 percent of total equivalised household disposable income with a decrease of 1.8 points compared with the previous year. This was followed by social transfers 21.9 percent with an increase 1.8 points and the entrepreneurial incomes 17.7 percent with a decrease of 1.1 points compared to 2018.
The share of agricultural income in the entrepreneurial income was realized as 22.6 percent by decreasing 0.3 points compared to 2018. Pensions and survivor' benefits comprised 91.8 percent of social transfers with an increase of 0.8 points compared to previous year.
Higher education graduates had the highest mean annual income at main job with 51 thousand 888 lira
Mean annual income at main job was calculated as 51 thousand 888 lira for higher education graduates, 34 thousand 115 lira for high or equivalent school graduates, 26 thousand 833 lira for those with less than high school education 18 thousand 279 lira for those who do not graduate from a school and 14 thousand 129 lira for illiterate individuals. In 2019, compared to 2018, the highest increase in income at the main job was observed in the illiterate individuals with 17.3 percent and the lowest increase was in literate individuals with no degree with 8.6 percent.
Construction sector held the highest increase of total income with 18.9 percent
When the mean annual income at main job are analyzed in branch of economic activity; it was observed that the highest mean annual income was in the service sector with 37 thousand 169 lira and the lowest mean annual income was in the agriculture sector with 21 thousand 807 lira. Compared to the previous year; the highest increase in mean annual income was observed in the construction sector with 18.9 percent, followed by the agricultural sector with 14.8 percent. On the other hand, an increase of 12.5 percent was observed in the service sector and 12.0 percent in the industrial sector.
Employers had the highest mean annual income at main job with 95 thousand 495 lira
Mean annual income at the main job was 95 thousand 495 lira for employers, 34 thousand 286 lira for regular employees, 27 thousand 127 lira for self employed workers and 14 thousand 769 lira for casual employees. Compared to the previous year, the highest increase was in regular employees with 13.9 percent and the lowest increase was in self employed workers with 8.2 percent.
Relative poverty rate was 14.4 percent
The people having incomes below a specified line compared to the general population is defined to be the poor in a relative meaning. The at-risk-of-poverty-rate according to poverty threshold set at 50 percent of median equivalised household disposable income was 14.4 percent with an increase of 0.5 points compared to 2018. As for the at-risk-of-poverty-rate according to the poverty threshold set at 60 percent of median equivalised household disposable income, it was 21.3 percent with an increase of 0.1 points in comparison with the previous year.
The at-risk-of-poverty-rate according to the poverty threshold set at 40 percent of median equivalised household disposable income was 8.3 percent with an increase of 0.4 points compared to the previous year and poverty threshold set at 70 percent of median equivalised household disposable income was 28.5 percent without a change.
One person households and multi-person no-family households had the lowest poverty rate
Considering poverty rates according to poverty threshold set at 50 percent of median equivalised household disposable income in terms of household types, at-risk-of-poverty-rate of one person households was 9.2 percent with a decrease of 0.4 points, multi-person no-family households was 9.2 percent with an increase of 1.5 points, extended family households was 18.2 percent with a decrease of 0.6 points and one-family households was 13.8 percent with an increase of 0.9 points compared to the previous year.
26.1 percent of illiterates and 2.5 percent of higher education graduates were poor
In terms of the at-risk-of-poverty-rate according to the poverty threshold set at 50 percent of median equivalised household disposable income, 26.1 percent of illiterates and 22.4 percent of literates with no degree were poor. The figures for less than high school and high school graduates were 13.4 percent and 6.9 percent respectively. Higher education graduates were the group with the lowest poverty rate with 2.5 percent.
Severe material deprivation rate was 26.3 percent
Material deprivation reflects to perception of households about inability to pay unexpected financial expenses, one week's annual holiday away from home, mortgage or rent payments, a meal with meat, chicken, fish every second day and heating home adequately warm and the ownership of a washing machine, a color TV, a telephone and a car.
The severe material deprivation rate defined as the rate of people faced with the enforced inability to afford at least four of the above-mentioned items decreased from 26.5 percent in 2018 to 26.3 percent in 2019.
Persistent at-risk-of-poverty-rate was 12.7 percent
The persistent at-risk-of-poverty rate shows the percentage of the population living in households where the equivalised disposable income was below the at-risk-of-poverty threshold set at 60 percent of median equivalised household income for the current year and for at least two out of the preceding three years. In 2019 the persistent at-risk-of-poverty-rate was 12.7 percent the same as the previous year.
Persistent at-risk-of-poverty-rate by 60 percent of median equivalised household income and percentage point change compared to the previous year, 2010-2019
The share of people living in their own dwellings was 58.8 percent
In 2019, the proportion of the population living in their own dwellings decreased by 0.2 point compared to the previous year, it was calculated as 58.8 percent while the share of those living in rented house was 25.6 percent, the share of those living in lodging was 1.3 percent and the share of those who did not pay rent despite not living in their own dwellings was 14.3 percent.
Inability of heating due to isolation was the most common housing and environmental problem
According to the 2019 results 39.3 percent of the non-institutional population had heating problems due to isolation. This ratio was calculated 36.9 percent for population faced with problems in their dwellings such as leaking roof, damp walls/floors/foundation, rot in window frames/floors and 26.1 percent for population had pollution, grime due to traffic/industry or other environmental problems.
Lowest income inequality was in East Marmara
S80/S20 ratio calculated as the ratio of total income received by the 20% of the population with the highest income to that received by the 20% of the population with the lowest income. As the ratio decreases, income inequality decreases.
According to the results of the latest research, while the SR Level 1 region with the lowest S80/S20 ratio was TR4 (East Marmara) with 4.6. It is followed by TR8 (West Black Sea), TR7 (Central Anatolia) regions with 5.5 and 5.6 respectively.
SR Level 1 region with the highest S80/S20 ratio was TR1 (İstanbul) with 7.8 and this region followed by TR6 (Mediterranean) region with 6.7 and TR2 (West Marmara) region with 6.6. (HA/VK)











